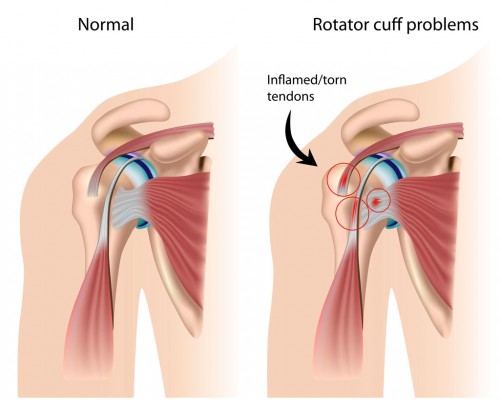
Tendonitis
Understanding Tendonitis: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
Tendonitis, also known as tendinitis, is a common condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when a tendon, the thick cord that attaches muscles to bones, becomes inflamed or irritated. This inflammation can lead to pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the affected joint. In this blog post, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and various treatment options for tendonitis.
- Causes of Tendonitis:
Tendonitis can be caused by a variety of factors, and understanding these triggers is crucial for effective management. Some common causes include:
Overuse or Repetitive Motion: Engaging in repetitive movements or overusing a particular joint can strain the associated tendons, leading to inflammation.
Poor Posture and Ergonomics: Incorrect posture or improper ergonomics during activities can contribute to the development of tendonitis.
Age: As we age, tendons become less flexible and more prone to injury, making older individuals more susceptible to tendonitis.
Sports Injuries: Athletes, especially those involved in sports that require repetitive motions or place excessive stress on specific joints, are at a higher risk of developing tendonitis.
Medical Conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis and diabetes, can increase the likelihood of developing tendonitis.
- Symptoms of Tendonitis:
Tendonitis often manifests with distinctive symptoms, which may vary depending on the affected area. Common signs include:
Pain: Tenderness and pain around the joint, particularly during movement or palpation.
Swelling: Inflammation of the affected tendon can lead to noticeable swelling in the surrounding area.
Stiffness: Tendonitis can cause stiffness and limited range of motion in the affected joint.
Warmth and Redness: The skin over the inflamed tendon may become warm to the touch and appear reddened.
- Treatment Options:
Managing tendonitis involves a combination of self-care measures and medical interventions. Here are some effective treatment options:
Rest and Immobilization: Giving the affected tendon time to heal by avoiding activities that aggravate the condition and using braces or splints to immobilize the joint.
Ice and Heat Therapy: Applying ice packs to reduce inflammation and heat packs to promote blood circulation can help alleviate pain and swelling.
Physical Therapy: Targeted exercises and stretching routines prescribed by a physical therapist can strengthen the affected tendon and improve flexibility.
Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen or naproxen can help manage pain and inflammation. In severe cases, a healthcare provider may prescribe stronger medications.
Corticosteroid Injections: Injections of corticosteroids directly into the affected tendon can provide quick relief from pain and inflammation.
Regenerative Therapies: Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and stem cell therapies are emerging as innovative treatments that may promote healing and reduce inflammation.
- Preventing Tendonitis:
While some factors leading to tendonitis may be unavoidable, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their risk:
Proper Warm-up and Stretching: Always warm up before engaging in physical activities and include appropriate stretches for the involved muscles and tendons.
Ergonomic Awareness: Maintain good posture and ergonomic practices, especially during work-related activities.
Gradual Increase in Activity: Avoid sudden increases in the intensity or duration of physical activities to give your body time to adapt.
Cross-Training: Vary your exercise routine to prevent overuse of specific muscle groups and tendons.
Conclusion:-
Tendonitis is a common condition that can significantly impact daily activities, but with proper understanding and management, individuals can experience relief and prevent future occurrences. If you suspect you have tendonitis, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and tailored treatment plan. Taking proactive steps to care for your tendons can contribute to a healthier, more active lifestyle.